GAT(Graph attention network)은 생각보다 오래전에 나왔다. 2018 ICLR(International Conference Learning Representation)에 발표되어, 현재 인용수만해도 3,000이 넘는다.
Key technical contribution
이전 그레프의 상태를 다음 그레프 상태에 Self-attention을 적용하여, 이전 그레프의 노드에 대한 다음 그레프의 노드의 중요도를 파악하는 것. 이를 attention coefficient 이라고함.
Attention coefficient: 아래와 같이 $h_{i}$(i번재 상태에서의 특징값)을 $h_{j}$번째의 상태에서의 특징값에 대해서 self-attention함. 결국 다음의 식에 따라, self-attention을 돌리고, 마지막에 attention weight을 곱하여, i번째의 상태의 그레프의 특징값을 반환

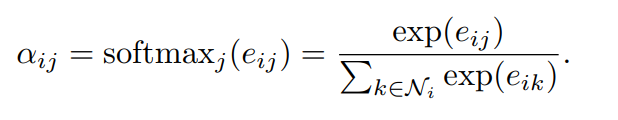

Multihead-attention coefficient: 저자들은 위의 attention coefficient을 k개를 만들어서 concat하는 방법으로 Multi-head attention을 계산도 해봄.

Single attention만 코드로 간략히 핵심만 구현하면 다음과 같다.
class GraphAttentionLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
'''
Single head attention GAT
Callable instance of class
Parameters
----------
input_dim: int. the number of feature space of given X
output_dim: int. the number of expected feature space
head_num: int. (defaualt 1)
Output
------
tf.Tensor (N, output_dim)
'''
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim, head_num=1):
super(GraphAttentionLayer, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.head_num = head_num
def build(self, input_shape):
'''
Parameters
----------
input: h = (N, F)
output: h' = (N, F')
Returns
-------
'''
# parameterized by a weight matrix W (F', F)
self.kernel = self.add_weight(shape=(input_shape[-1], self.output_dim), name='W') # W:(F, F')
# Parameterized by a weight vector a (2F')
self.a = self.add_weight(shape=(2*self.output_dim, 1), name='a')
self.built = True
def call(self, X):
# Eqation 1) mapping F feature space to F' features space
features_i = tf.einsum('ij,jk->ik', X, self.kernel) # (NxF) (FxF') => WH_i (NxF')
features_j = tf.einsum('ij,jk->ik', X, self.kernel) # (NxF) (FxF') => WH_j (NxF')
# Equation 3) Attention coefficient
e_ij = tf.tensordot(tf.concat([features_i, features_j], axis=1), self.a, axes=1)
a_ij = tf.nn.softmax(e_ij, axis=0) # (N,1)
# Equation 4) Applying non-linearity with sigma
context_vec = tf.einsum('ij,ik->ik', a_ij, features_i) # (N,1) (NxF')
h = tf.nn.sigmoid(context_vec, name='attention_coefficient')
return h
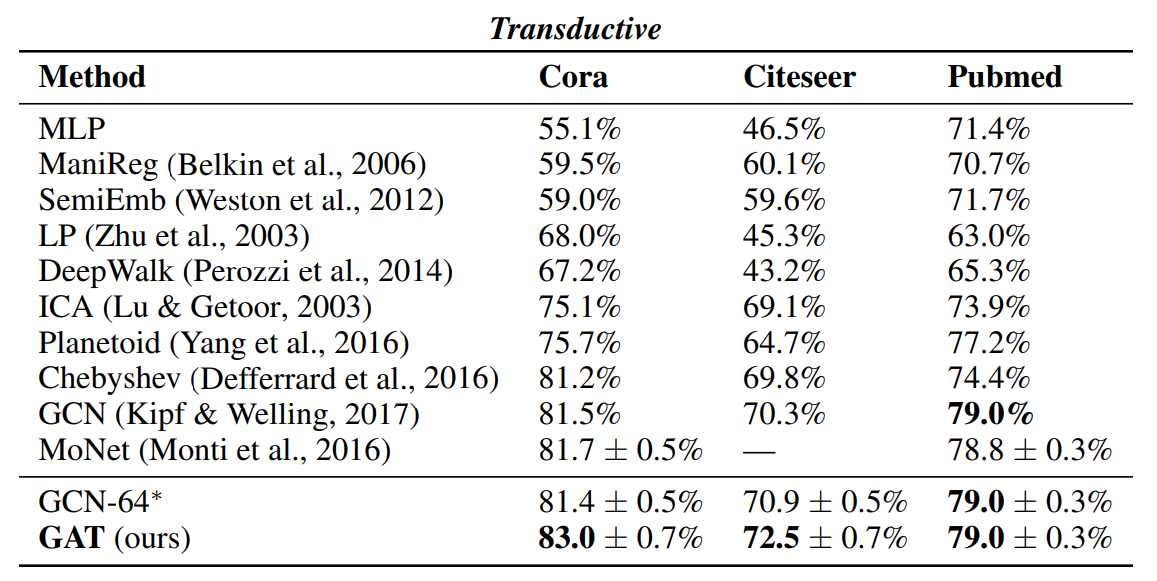
모델성능: 성능은 Transductive, inductive 두 가지 방법으로 설명함. (Transductive, inductive을 모른다면, 다음의 포스팅을 클릭). 1) Transductive dataset은 Cora, Citeseer, Pubmed라는 논문 인용에 관한 데이터. Node: 논문, edge: 인용. Node feature: Bag of words in document. Node label: class label. 2) Inductive learning: PPI(단백질-단백질-교호작용) 데이터세트. 그레프 분류

텐서플로2.0 으로 구현한 소스코드와 설명은 다음을 참조
'Best Paper review > Others' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자연어처리의 고전 BERT, 5분 컷 이해 (0) | 2021.10.25 |
|---|---|
| ICLR 2018: FEW-SHOT LEARNING WITH Graph 풀이 (0) | 2021.06.22 |
| 2019 best paper: Ordered Neurons 해석 (0) | 2021.06.21 |
| Batch normalization 추론모드에서 사용? (0) | 2021.06.01 |
| Transformer (트랜스포머) 해석 (0) | 2021.05.13 |



